About GAVRETO
Mechanism of action (MOA)
GAVRETO is a potent and selective inhibitor for RET1
GAVRETO exhibited anti-tumor activity in cultured cells and animal tumor implantation models harboring oncogenic RET fusions or mutations1*
In cellular assays, GAVRETO inhibited RET at approximately 14-, 40-, and 12-fold lower concentrations than VEGFR2, FGFR2, and JAK2, respectively.1
GAVRETO prolonged survival in mice implanted intracranially with tumor models expressing KIF5B-RET or CCDC6-RET.1
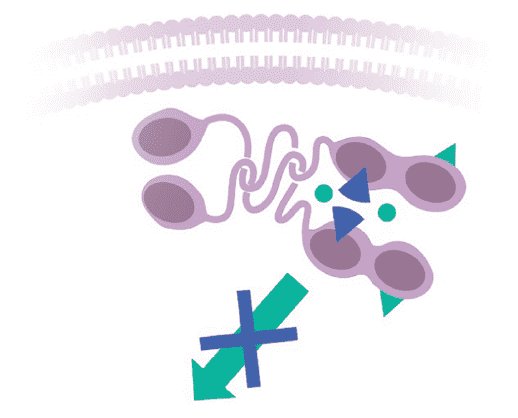
Tumor growth
and proliferation
GAVRETO
Primary mutants and resistant mutants
ATP
*Mutations including KIF5B-RET, CCDC6-RET, RET M918T, RET C634W, RET V804E, RET V804L, and RET V804M.1
ATP=adenosine triphosphate; CCDC6=coiled-coil domain containing 6; JAK2=Janus kinase 2; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; RET=rearranged during transfection; VEGFR2=vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®)-recommended first-line treatment option2*
When RET fusion is identified prior to first-line treatment, initiate pralsetinib (GAVRETO)2
When RET fusion is discovered during first-line systemic therapy, interrupt current treatment and initiate pralsetinib (GAVRETO)2†
*See the NCCN Guidelines® for NSCLC for detailed recommendations, including other preferred options.
†If there is a good response to current therapy, it is reasonable to continue therapy.
NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
See RET+ mNSCLC
efficacy data
Uncover the results for patients treated with a RET inhibitor.
GAV_LNG-25014 0525
References:
1. GAVRETO® [Package insert], South San Francisco, CA: Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
2. Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.7.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All rights reserved. Accessed July 10, 2025. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.